
Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays are particles in nature. Thomson's determination of the charge to mass ratio of cathode rays settled the debate of the nature of cathode rays. Applied Surface Science Development of the EXITE Detector: A. Therefore, they have mass and are particles in nature. What scientist did the cathode ray experiment Emission ability of LaScMo cathode. Conclusion: cathode rays have momentum and kinetic energy.Observation: when the glass paddle wheel was struck by the cathode ray, it rotated and moved towards the cathode.What was done: a glass paddle wheel that could move and rotate freely was placed in the path of the cathode ray.Conclusion: cathode rays are streams of negatively charged particles.In the presence of a magnetic field, the path of the cathode ray was deflected in a direction that was consisted with a negatively charged mass. Observation: in the presence of an electric field, the path of the cathode ray was deflected towards the positively charged plate.

What was done: a metal plate coated with fluorescent material was used to visualise the trajectory of a cathode ray. The cathode ray was passed through a uniform electric field and magnetic field (in separate experiments).However, this observation could also be produced by particles.Ĭathode Ray Tubes Containing Electric and Magnetic Fields Some scientists argued that since waves such as light can produce a similar observation, cathode rays are wave in nature. Conclusion: Cathode rays travel in a straight line and can cast a shadow.Observation: a shadow of the maltese cross was formed directly behind the anode.
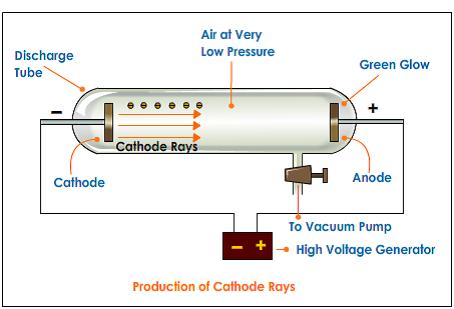

It is important to keep in mind that at the time when cathode rays were observed, scientists were not aware of the existence of electrons. In a near-vacuum setting where there are few to none air molecules, these electrons can travel unimpeded.Ī simple representation of a cathode ray tubeĪ cathode ray was the name given to the observation of these electrons when they were incident on the glass coated with fluorescent material behind the cathode. The high potential difference causes electrons to move from the anode to the cathode. Similar to a discharge tube, a cathode ray tube consists of two electrodes connected to a high potential difference. The positive electrode is the anode, and the negative electrode is the cathode. Cathode rays were produced in partially evacuated discharged tubes called Crookes tubes (cathode ray tubes).Ī simple representation of a gas discharge tube


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
